Artificial intelligence is everywhere, from the apps on your phone to the systems powering global businesses. But not all AI is created equal. The type of AI we interact with most today is called narrow AI, also known as artificial narrow intelligence (ANI).
Narrow AI refers to AI systems designed for a specific task. Whether that’s generating text, detecting fraud, or recognizing images, these models excel within a defined scope. In fact, nearly all of the AI you use daily, from recommendation engines to customer service chatbots, belongs in this category.
In this guide, we’ll explain what narrow AI is, how it differs from general AI, and where it’s already making an impact. We’ll also explore how platforms like Vertical make it possible for businesses and creators to harness narrow AI in powerful, practical ways.
What Is Narrow AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence)?
At its core, narrow AI describes systems built to handle one particular function. Unlike human intelligence, which can reason across many contexts, narrow AI stays within its lane.
Key characteristics of narrow AI:
Designed for a specific task (e.g., classifying images, predicting text, recommending products).
Optimized for high accuracy within its domain.
The most common and widely deployed form of AI today.
Powers many of the tools businesses rely on for efficiency and automation.
When you hear about foundational models like ChatGPT, Claude, or DeepSeek, you’re looking at narrow AI systems that have been trained and fine-tuned for text-based tasks.
Narrow AI vs General AI: What’s the Difference?
To understand narrow AI, it helps to compare it with what’s often seen as its next evolution: artificial general intelligence (AGI). AGI would replicate the full range of human intelligence, but it doesn’t exist yet. Narrow AI is already here: practical, reliable, and delivering results in business today.
Feature | Narrow AI | General AI (AGI) |
Scope of Tasks | Performs a single or limited task | Can perform any intellectual task a human can |
Example Use Cases | Chatbots, image recognition, spam filters | Hypothetical human-like assistants or robots |
Flexibility | Task-specific, cannot adapt beyond training | Highly adaptable across domains |
Learning Ability | Learns within predefined parameters | Learns and reasons across unrelated tasks |
Existence Today | Widely used and deployed | Still theoretical, under development |
Risk Profile | Lower risk, easier to control | Higher ethical and technical risks |
Key Advantages | Reliable, efficient, easy to deploy in real-world use | Aspirational intelligence, could surpass human capabilities |
Real-World Examples of Narrow AI
Narrow AI isn’t just a concept, it’s woven into the tools we use every day, often so seamlessly that we barely notice it. Some familiar examples include:
Chatbots: From airline websites to banking apps, AI-powered bots answer questions, troubleshoot problems, and keep support lines moving quickly.
Recommendation engines: Think Netflix lining up your next binge-worthy series or Amazon suggesting products you didn’t know you needed.
Image recognition: Whether it’s unlocking your phone with facial ID or analyzing medical scans for early signs of disease, this technology is now routine.
Language models: Tools like ChatGPT help draft emails, generate code or summarize reports, accelerating everyday tasks across industries based on your prompt.
What ties these systems together is their focus. Each is trained to excel at one specific task, and that specialization is exactly what makes narrow AI so effective.
Benefits and Limitations of Narrow AI
However, like any technology, narrow AI brings both advantages and limitations. Its strength lies in doing one job extremely well, but that focus also means it can’t easily step outside its defined role. The key takeaway is that narrow AI becomes most powerful when applied to a clearly defined problem, where its precision and efficiency can shine.
Benefits | Limitations |
High efficiency in specific tasks | Cannot perform tasks outside its domain |
Accurate results within set parameters | Lacks general reasoning |
Specialization leads to better performance | Rigid and doesn’t easily adapt to new contexts |
Proven effectiveness in real-world use | Limited scalability beyond original use case |
Why Narrow AI Matters for Businesses and Creators
For businesses, narrow AI is far more than a passing buzzword, it’s becoming a practical driver of transformation. Companies are already using it to streamline industry-specific tasks, from reviewing legal documents with precision to assisting doctors in medical diagnostics. It’s also reshaping customer engagement: chatbots now handle everyday inquiries, personalization engines tailor experiences and sentiment analysis tools help brands understand their audiences better. Behind the scenes, narrow AI is boosting operational efficiency by automating repetitive workflows, reducing costs, and freeing teams to focus on higher-value work. Perhaps most importantly, domain-specific models are exposing insights that generic tools often overlook, giving organizations a sharper edge.
And it’s not just businesses that benefit. For creators and developers, narrow AI is an opportunity to build highly specialized models that solve real problems. Think of a customer support bot fine-tuned for the insurance industry, a model that analyzes contracts for specific legal clauses, or an AI trained to generate marketing copy in a brand’s unique tone of voice. These kinds of focused tools go beyond what broad, general-purpose systems can deliver. This shift marks a turning point where AI isn’t just consumed, but actively shaped by those who create with it but actively shaped to meet specialized needs.

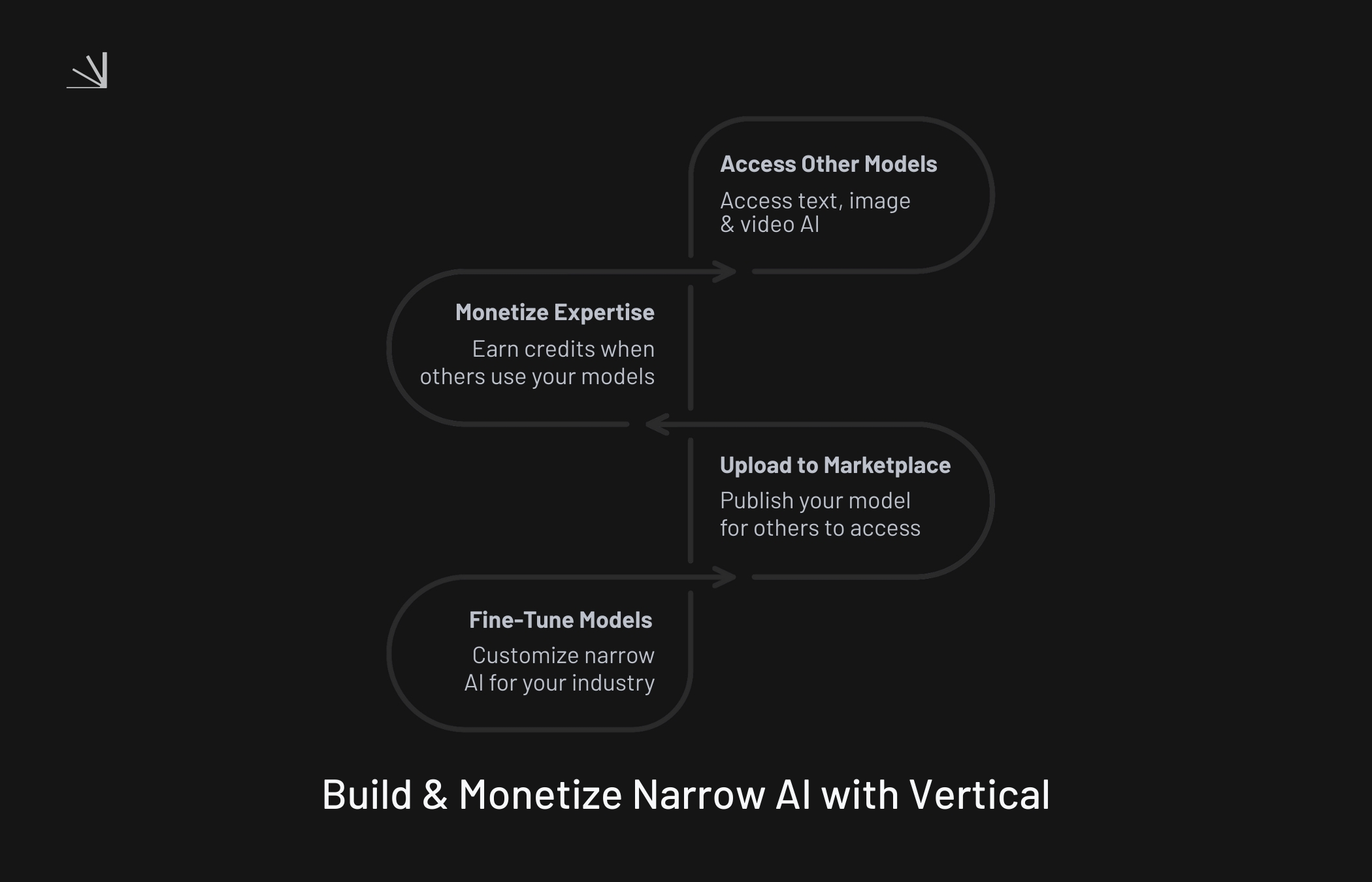
Fine-Tune Narrow AI Models on Vertical
This is where Vertical comes in. Unlike platforms that only provide access to prebuilt models, Vertical empowers users to become AI creators.
On Vertical, you can:
Fine-tune narrow AI models for your specific use case (for example, a customer support bot for the insurance sector or a medical language model).
Upload your models to the Vertical marketplace, making them available to others.
Monetize your expertise by earning credits when others use your models.
Access a wide range of AI models, from text to image and video, to integrate into your workflows.
This ecosystem bridges the gap between businesses seeking tailored AI solutions and creators building them. By focusing on narrow AI innovation, Vertical helps both sides maximize value from the technology.